ADVERTISEMENT
Eating oatmeal for breakfast can be extremely comforting and not to mention guilt-free. Made with a blend of oats and water or oats and milk, the mighty oatmeal is a fiber powerhouse. Packed with nutrition, oatmeal is a choice you really can’t go wrong with. Plus, there’s tons of customization options for toppings from berries to nuts.
If you aren’t eating oatmeal everyday, perhaps the following reasons will make you think otherwise. Here’s what happens to your body once you take a bite of oatmeal.
1. Lower cholesterol
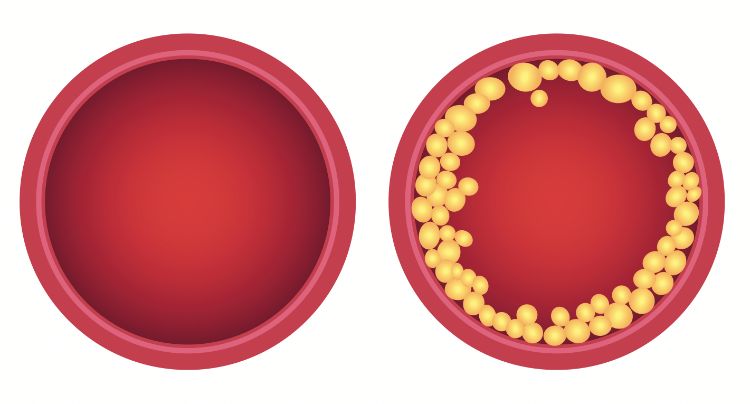
More importantly, oatmeal can lower LDL cholesterol, the “bad” cholesterol associated with clogging arteries and increased heart disease risk. Research has shown oatmeal to lower LDL cholesterol by an average of 7%. Why is this? Oatmeal is made of soluble fiber. This fiber produces a viscous gel, helping reduce cholesterol.
2. Stabilize or lower blood sugar
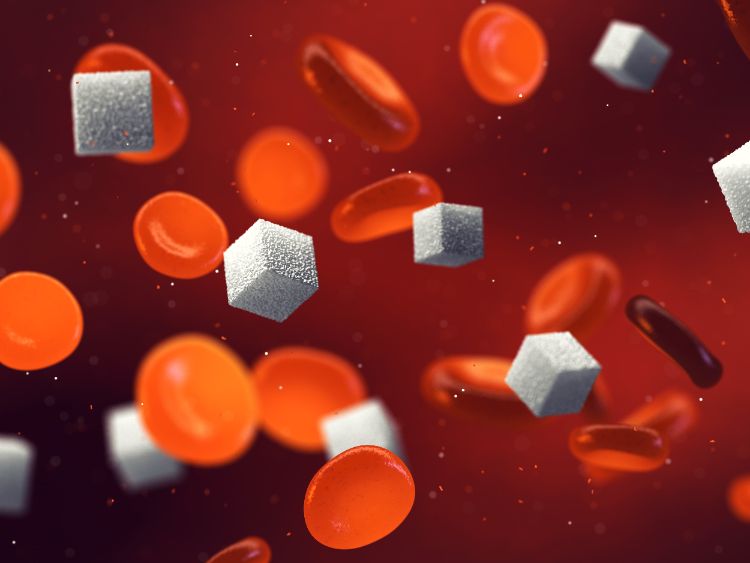
The soluble fiber of oatmeal also helps stabilize or reduce blood sugar levels, particularly after consumption. For people with diabetes, less-processed oats have a low to medium glycemic load, but instant oatmeal should be avoided.
Pro-Tip: Not all oatmeal is the same. Steel-cut oats (or Irish oatmeal), pictured below, are the best. They are the most unprocessed of the oats, meaning they are richer in fiber compared to rolled or quick oats. Try to avoid instant oatmeal as that can contain skim milk powder, sugar, and other additives.

3. Give you nutrients and minerals
Oatmeal is high in many nutrients and minerals, including magnesium, zinc, vitamin B1, manganese, phosphorus, copper, selenium, and iron.
4. Weight control
see continuation on next page
For Complete Cooking STEPS Please Head On Over To Next Page Or Open button (>) and don’t forget to SHARE with your Facebook friends
ADVERTISEMENT
